Doha 2015 Newsletter - Understanding Para-Athletics: T44 Classification
T44 Classification (Please find Arabic text below) 25 Sep 2015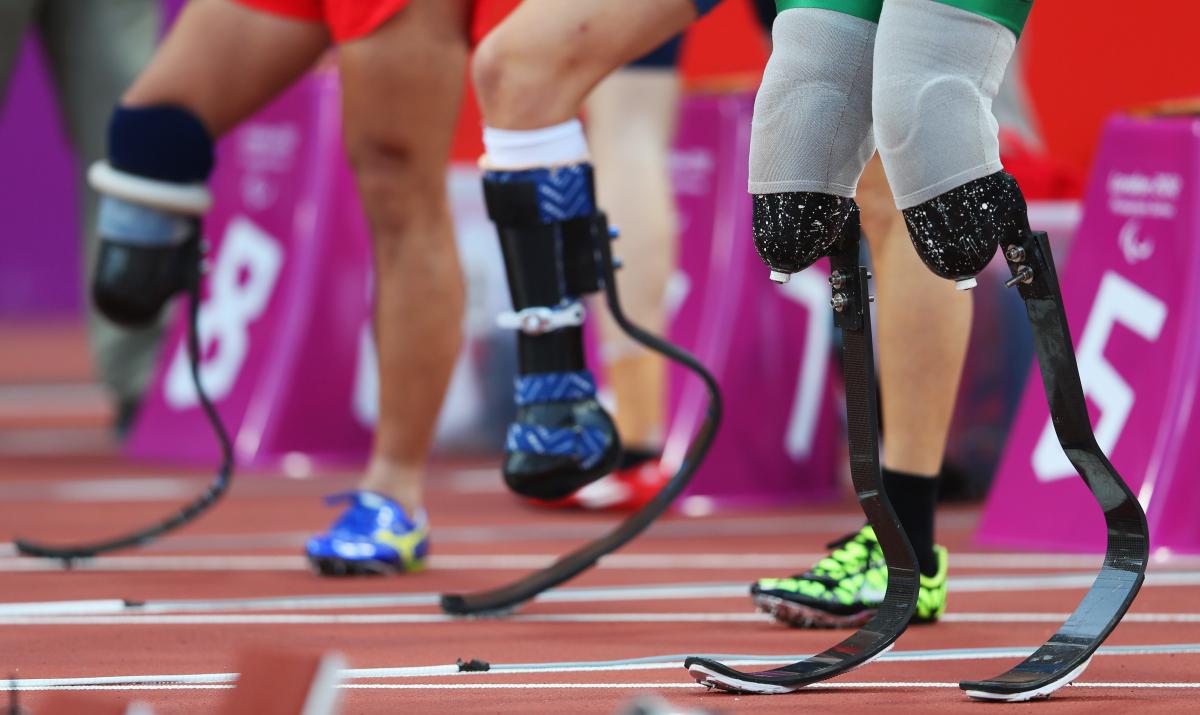
A view of the prosthetics legs of Alan Fonteles Cardoso Oliveira of Brazil during the London 2012 Paralympic Games.
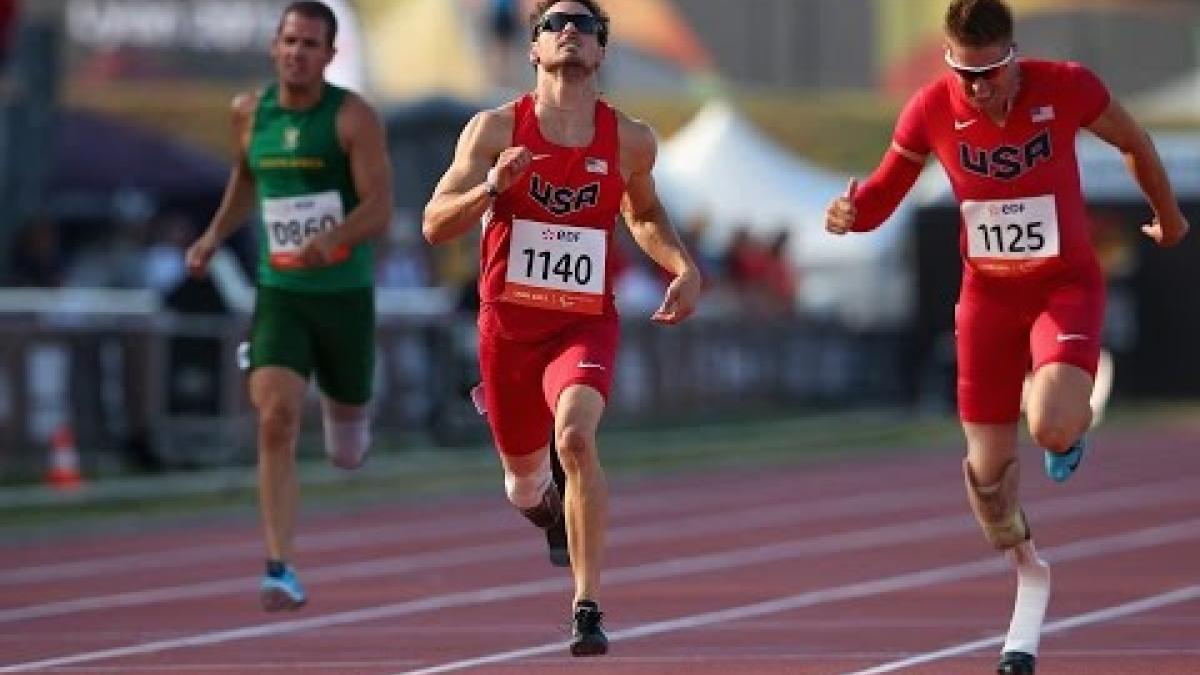
IPC Sport Classification aims to minimize the impact of impairments on the sporting discipline, with a prefix of “T” used to denote track/jump events while the “F” prefix is used to indicate field events. This week’s “My Incredible Story” focuses on Jarryd Wallace who competes in the T44 Classification after the amputation of his right leg below the knee due to complications resulting from compartment syndrome.
Athletes competing in T44 Classification events, such as world-record holder Wallace, have a single below knee amputation or walk with moderately reduced function in one or both legs. This class is for any athlete with lower limb impairments that meet the minimum disability criteria for lower limb deficiency, impaired lower limb passive range of motion, impaired lower limb muscle power or leg length difference.
Notable athletes that compete under the T44 classification include April Holmes, who holds the world record in the T44 100m event and French runner Marie-Amelie Le Fur who holds the 200m, 400m and 800m world records. Meanwhile Jarryd Wallace holds the world record in the 100m, 200m and 4x100m T44 events.
Wallace competes under the T44 Classification after surgery to correct the effects of Compartment Syndrome left him lacking 60% of the muscle in his right leg. The runner decided to amputate his leg in 2010 after being informed by his doctor that the loss of his leg would ultimately be inevitable.
Compartment Syndrome is increased pressure within the body’s compartments which contains muscles and nerves. Compartment Syndrome usually occurs in the leg or the arm and may be acute – as a result of a traumatic injury such as a car accident – or chronic – which is an exercise-induced condition in which pressure builds in the muscles during exercise. In both types of Compartment Syndrome, which causes extreme pain, the pressure creates a decrease in blood flow to the affected area which leads to oxygen deprivation in the muscles. If left untreated, Compartment Syndrome leads to permanent muscle and nerve damage and can result in the loss of function in the limb.
_____
تصنيف T44
وُضِعَ نظام التصنيف مِن قِبل اللجنة البارالمبية الدوليّة للحد من تأثير الإعاقة على الانضباط الرياضيّ. ويتكونُ التصنيف من البادئة "T" لرياضة المضمار/الوَثْب والبادئة "F" للمنافسات الميدانية. وتسلط سلسلة أفلام "قصتي التي لا تصدق" هذا الأسبوع على جاريد والاس الذي ينافس في فئةT44 بعد بتر ساقه اليمنى من أسفل الركبة بسبب مضاعفات ناتجة عن متلازمة الحجرات المضغوطة.
يعاني الرياضيون الذي يتنافسون ضمن الفئة T44، مثل حامل الرقم القياسي العالمي والاس، من بتر أسفل الركبة، أو بإمكانهم المشي لكن بضعف في وظائف إحدى أو كلتا الساقين. هذه الفئة مخصصة لأي رياضي يعاني من إعاقات في الأطراف تلبي الحد الأدنى لمعايير الإعاقة المتعلقة بالعجز في الأطراف، أو الضعف السلبي لحركة الطرف السفلي، أو ضعف عضلات الأطراف، أو وجود فروق بين طول الساقين.
وتشهد الفئة T44 منافسات بين رياضيين مشهورين، من بينهم أبريل هولمز، الذي يحمل الرقم القياسي العالمي في سباق 100 متر والعدّاء الفرنسي ماري اميلي لو فور الذي يحمل الأرقام القياسية العالمية في سباقات 200 متر، و400 متر، و800 متر. وفي الوقت نفسه، جاريد والاس الذي يحمل الرقم القياسي العالمي في سباقات 100 متر، و200 متر و4x100 متر.
بدأ والاس في المنافسة ضمن الفئةT44 بعد خضوعه لعملية جراحية لتصحيح آثار متلازمة الحجرات المضغوطة والتي أدت إلى خسارته 60٪ من عضلات ساقه اليمنى. بعدها قرر العدّاء بتر ساقه في عام 2010 حين أبلغه طبيبه أن فقدان ساقه أصبح أمراً حتمياً.
تُعد متلازمة الحجرات المضغوطة عبارة عن زيادة في الضغط داخل مقصورات الجسم والتي تحتوي على العضلات والأعصاب. وعادة ما تحدث هذه المتلازمة في الساق أو الذراع، وربما تكون حادة – ناتجة عن إصابة مؤلمة مثل حادث سيارة - أو مزمنة - وهي حالة تتعلق بممارسة الأنشطة حيث يتراكم الضغط في العضلات أثناء ممارسة الرياضة. وفي كلا النوعين تتسبب المتلازمة في ألم شديد، ويؤدي الضغط إلى انخفاض في تدفق الدم إلى المنطقة المصابة مما يؤدي إلى نقص الأكسجين في العضلات. وإذا تركت هذه الحالة العلاج، فقد تؤدي إلى تلف دائم في العضلات والأعصاب أو فقدان وظائف الأطراف كاملة.

 Facebook
Facebook
 Instagram
Instagram
 Twitter
Twitter
 Youtube
Youtube




