Para athletics classification explained
A beginner’s guide to classification in the sport of Para athletics. 05 Mar 2017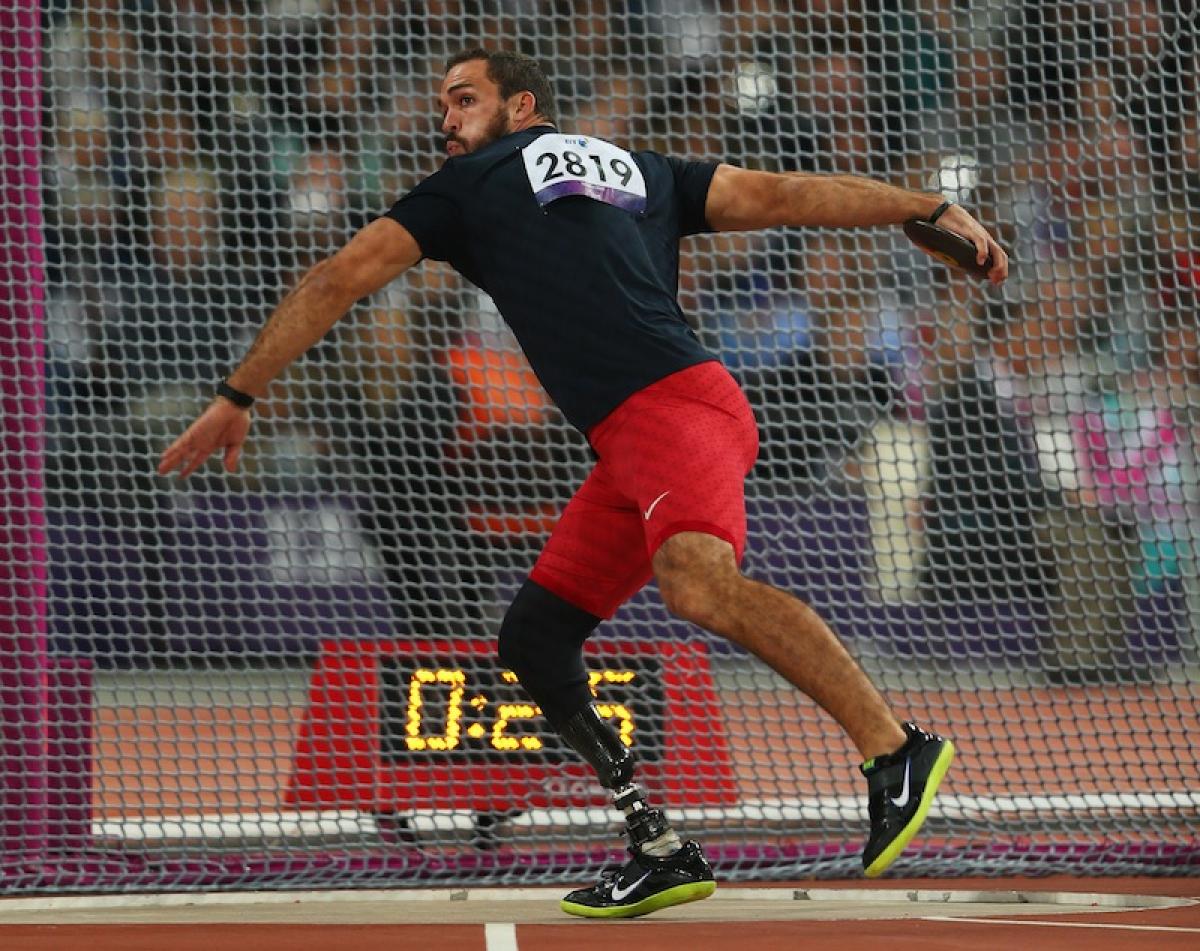
Jeremy Campbell at London 2012.
With the new 2017 now upon us, here’s a chance to remind yourself exactly how the different classes in World Para Athletics are defined.
The World Para Athletics classification system serves two key purposes:
1. Determining eligibility: defining who is eligible to compete in World Para Athletics competitions.
2. Sport class allocation: specifying ways to divide eligible athletes up into sport classes. The aim is that each class should consist of athletes who have impairments that cause approximately the same amount of activity limitation in the key athletic disciplines – running, wheelchair racing, jumps and throws.
A classification panel allocates each athlete with a sport class – however, athletes may not remain in the same class for their entire Para athletics career; due to the progressive nature of some impairments and their impact on certain activities, athletes are sometimes classified a number of times.
Classes are given a number, and each number is prefixed with either a ‘T’, which stands for ‘track’, or an ‘F’ for ‘field’.
Impairments are split into groups – for example visually impaired athletes are in the tens (T11, T12 and T13); athletes with co-ordination impairments are in the thirties (T31-38).
The number also represents the level of impairment; the lower the number within each impairment type, the more severe the impairment.
Running and jumping (16 classes)
T11-13 (Visual impairment)
T20 (Intellectual impairment)
T35-38 (Co-ordination impairments)
T40-41 (Short stature)
T42-44 (Lower limb affected by limb deficiency, leg length difference, impaired muscle power or impaired range of movement)
T45-47 (Upper limbs affected by limb deficiency, impaired muscle power or impaired range of movement)
Wheelchair racing (7 classes)
T32-34 (Co-ordination impairments)
T51-54 (Limb deficiency, leg length difference, impaired muscle power or impaired range of movement)
Standing throws (15 classes)
F11-13 (Visual impairment)
F20 (Intellectual impairment)
F35-38 (Co-ordination impairments)
F40-41 (Short stature)
F42-44 (Lower limb affected by limb deficiency, leg length difference, impaired muscle power or impaired range of movement)
F45-46 (Upper limb/s affected by limb deficiency, impaired muscle power or impaired range of movement)
Seated throws (11 classes)
F31-34 (Coordination impairments)
F51-57 (Limb deficiency, leg length difference, impaired muscle power or impaired range of movement)

 Facebook
Facebook
 Instagram
Instagram
 Twitter
Twitter
 Youtube
Youtube





