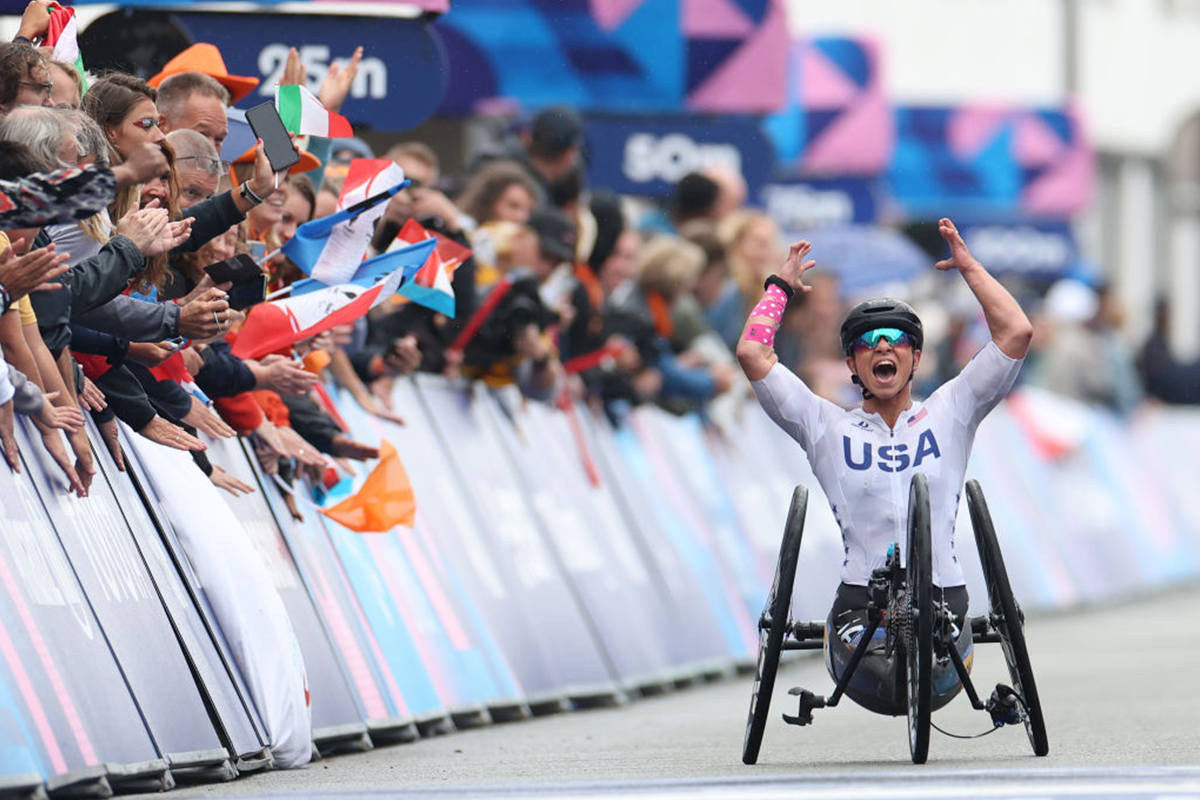

Para Cycling
In individual pursuit events, riders start on opposite sides of the track and attempt to catch up to their opponent over the course of 12 or 16 laps.
About Para Cycling
The Paralympic Para cycling competition programme includes sprints, individual pursuits, road races and road time trials for both individuals and teams. Distances of competition events range from 200m sprint to 15km road races.
Athletes compete on three different modes of equipment, bicycles, tricycles, and handcycles. Athletes that compete in Para cycling include those with vision impairments or physical impairments.
There are five sport classes for hand cycling (H1-H5), two for tricycle (T1-T2) and five for bicycle (C1-C5), whilst the three sport classes for the tandem compete in one event (B1-B3).
Within the sport, some events welcome athletes from different classes. The process of factoring is used to adjust an athlete’s time based on their degree of classification, allowing for a combined ranking of cyclists from different classes. The fastest factored time wins the medal, as it represents the athlete's performance relative to the challenges of their class.
Para cycling is governed by the Union Cycliste Internationale (UCI).
Para cycling history
Para cycling began in the 1980s, with athletes with disabilities competing alongside non disabled riders. It was used for rehabilitation recorded as far back as 1949. Initially, some of the first riders were those with vision impairments known as stokers riding tandem with a sighted pilot guiding the bike.
Road Para cycling made its Paralympic debut at New York/Stoke Mandeville 1984, hosting events for those with cerebral palsy. Para cycling has taken place at every Games since its debut.
Initially only 22 athletes competed in the Stoke Mandeville/New York Games, but 40 athletes were showcased in the next edition of the games in Seoul 1988, demonstrating its meteoric rise.
Road cycling has taken place at every Paralympic Games since 1984, but track cycling was added to the Paralympic sport programme at the Atlanta 1996 Paralympic Games.
In 2000, during the Sydney 2000 Paralympic Games, the sport’s popularity was cemented when 200 athletes participated in Para cycling for the first time.
The most recent change to Para cycling was the addition of the mixed team relay in London 2012.
The Tokyo 2020 Games hosted the most countries in history with 51 events, 50 countries and 230 competitors. Although the Rio 2016 Games showcased the most athletes at 235.
Did you know ?
The teams in a team sprint event can consist of male and female Para athletes. The teams may also include different classes of athletes. Based on the classification and gender, the team’s final score may be adjusted in the race on the factoring principle.
Video
Para Cycling News
View more
Best Para cycling moments of Paris 2024
Jetze Plat won two Para cycling road gold medals to add to a Paralympic triathlon title

Para cycling moves from track to road on Day 7
Sarah Storey and Oksana Masters headline the Para cycling road competition, with four golds up for grabs in Para powerlifting and the first Paris 2024 wheelchair tennis champions to be decided on Day 7
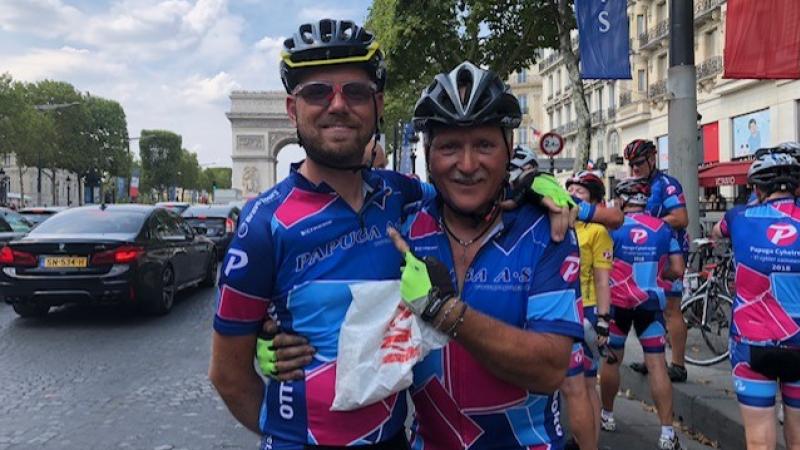

Heggelund no stranger to cycling in France
Years after an epic 1000 kilometre tandem bike adventure from Denmark to France, Martin Heggelund will don the red and white in Paris
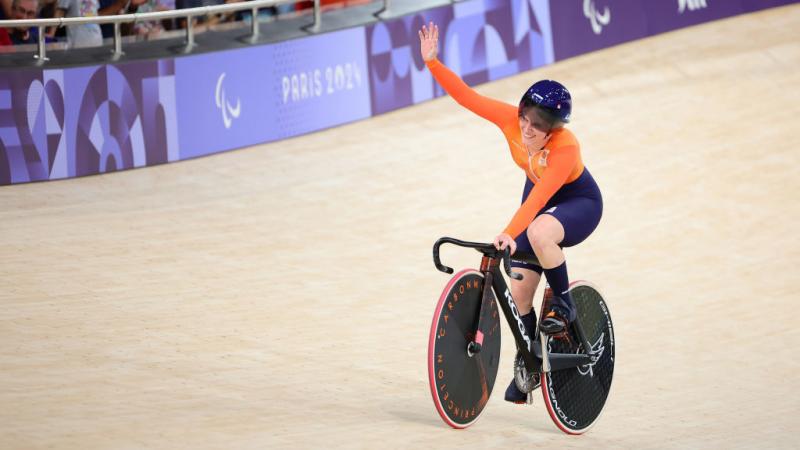
Para cyclist Groot wins first gold medal of Games
Caroline Groot of the Netherlands won gold in the Para cycling track but is quitting to become a lawyer
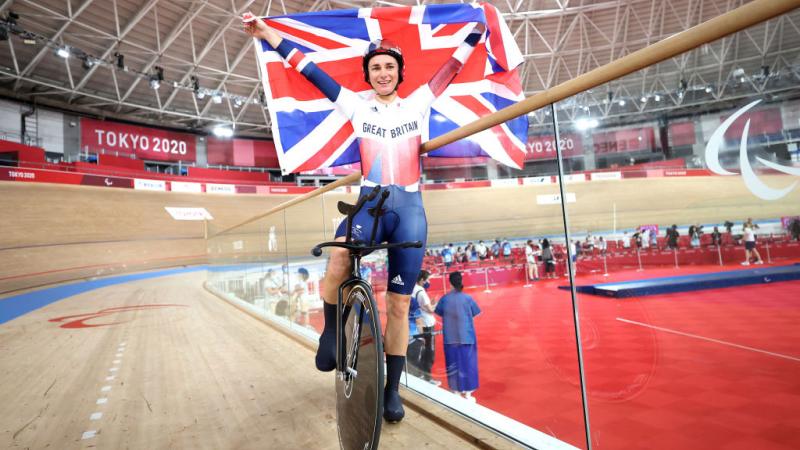

Sarah Storey wants to create more history at her ninth Paralympics
From preparation for Paris 2024, motherhood and winning 17 Paralympic gold medals, Britain’s greatest Paralympian shares how she does it all
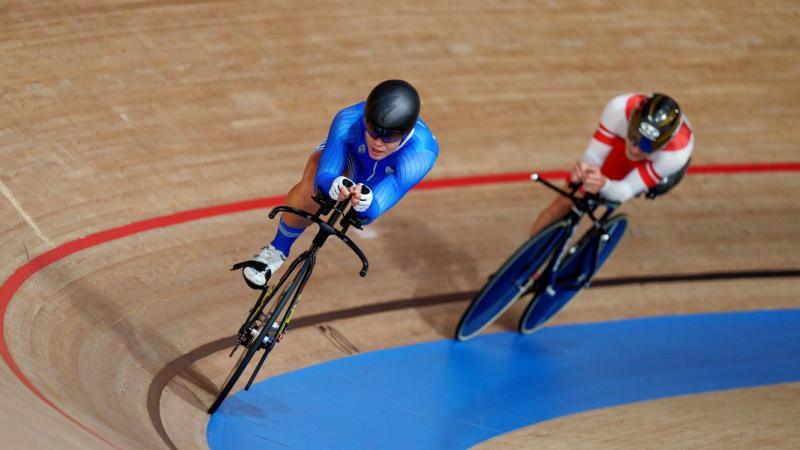

Introduction to Para cycling
Paris 2024 Paralympics will feature up to 220 athletes competing in 51 medal events
Federation Contact
Para cycling
Todd Fraser
PARALYMPIC AND PARA SPORT RESULTS
Search for all results from Paralympic Games events and selected other international Para sport events.
Para Cycling FAQ
Para cyclists have a wide range of disabilities. There are 15 different sport classes, ranging from significant physical limitation in lower and upper limbs to vision impairment with no other physical disability. This is the reason tricycle, bicycle, and hand bike are all offered as competition events in the Paralympics.
Anyone with a physical disability or vision impairment can compete in Para cycling. Further details of classification are available.
Para athletes may use four different types of bikes depending on their disability and classification. Specifically, tricycles, bicycles, tandem bicycles, and hand cycles are eligible to use in competition.
The pilot in Para cycling acts as a guide for cyclists with visionimpairments. The pilot sits in the front of a tandem bike, steering, while the stoker (the visually impaired athlete) sits in the back of the bike.
The distances in Para cycling greatly differ depending on the discipline. Sprints are usually shorter distances.
Track individual pursuit is 3km to 4km.
Track sprint is 200m.
Track time trial is 500m to 1km.
Track team sprint is 750m
Road race is 7km to 15km.
Para cycling operates in a competition format where the fastest cyclist in any event wins. There are 15 classifications and many events including time trials, road races, tandem sprints, team sprints, and individual pursuits that athletes may compete in.
The time trial for Para cycling includes solo or tandem cyclists racing on relatively short distances. The cyclists who complete the course the quickest in the winner.
The pilot is the sighted cyclist on a tandem bike, sitting at the front to steer. The stoker is the vision impaired athlete that sits at the back of the bike.
Para track cycling offers multiple events, including time trial, tandem sprint, team sprint, and individual pursuit. Each discipline has separate rules, but each are performed on a track rather than the road.



